Micro Quick Response (QR) Codes
Micro QR Code
The Quick Response (QR) code was revolutionary for its ability to store far more information than was possible with traditional, one dimensional barcodes. In some use cases, this ability to encode so much data makes the QR Code larger than necessary. That’s why Denso Wave created a smaller, more compact version in 1994 called the Micro QR Code. The code is frequently used to track very small components like circuit boards and other electronic parts. Micro QR Code is a public domain 2D barcode covered under the ISO/IEC 18004:2015 standard. Like their bigger cousins, Micro QR Codes can encode Japanese Kanji, Kana, and Hiragana characters.
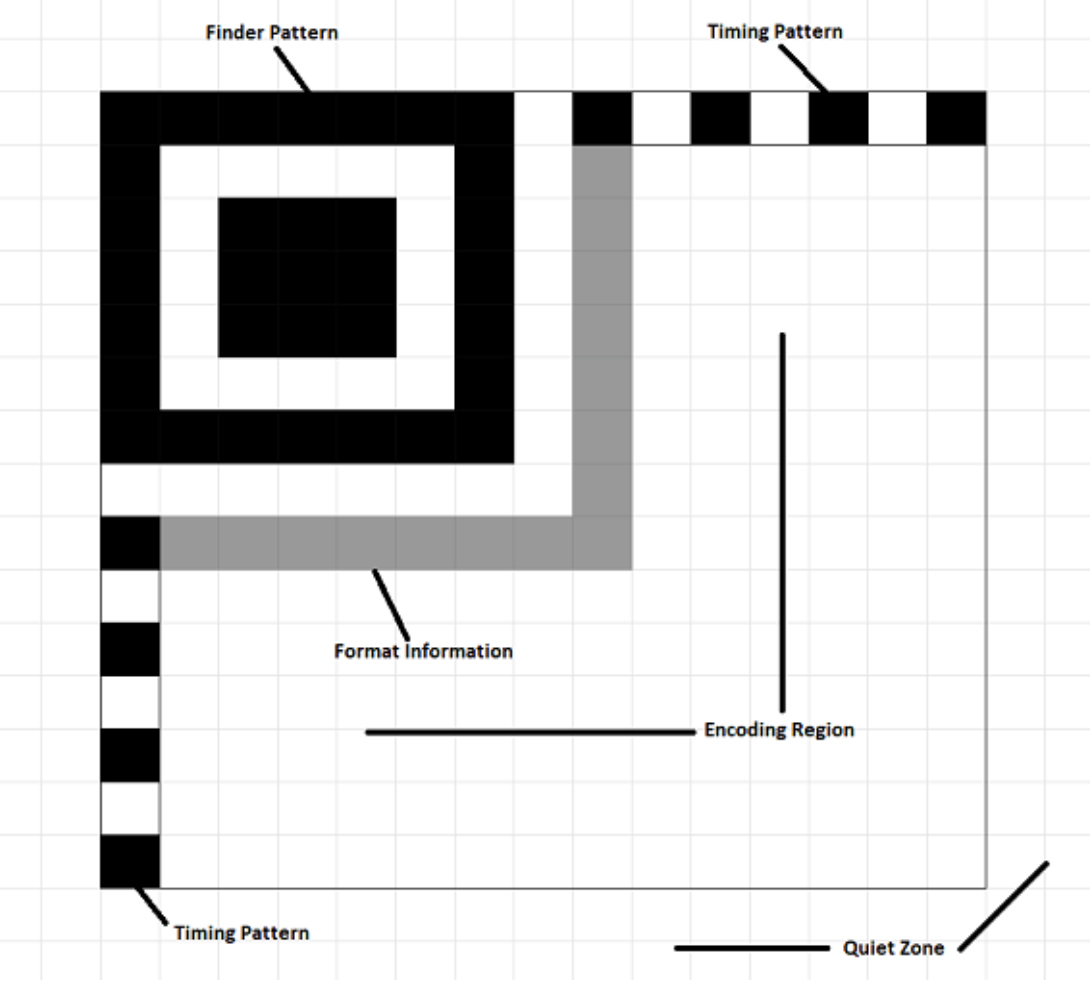
While a conventional QR Code uses three finder pattern squares to enable barcode readers to orient the image properly, a Micro QR Code uses a single finder pattern square in the upper-left corner. It also requires only a two-module wide “quiet zone” around the edge of the symbol, as opposed to the four-module wide margin needed for a regular QR Code. These differences, along with the fact that Micro QR Codes encode data more efficiently, prevent the code from becoming much larger even as the amount of data stored increases, which is a challenge with regular QR Codes.
Format
Each Micro QR Code consists of four elements:
- Square modules that contain data.
- A finder pattern to indicate the code’s orientation.
- A timing pattern to indicate the code’s version and density.
- A “quiet zone” border surrounding the modules.
Data itself is encoded in modules, or the square dots that represent binary data. A black module represents a binary 1, while a white module represents a binary 0.
Micro QR Codes can be written in four different sizes. The smallest of which, Version M1, consists of 11 x 11 modules while the largest, Version M4, contains 17 x 17 modules and can store up to 128 bits. Each version offers different levels of error correction based on the Reed-Solomon algorithm:
- Level L (Low): 7% of data can be recovered
- Level M (Medium): 15% of data can be recovered
- Level Q (Quartile): 25% of data can be recovered
As with regular QR Codes, adding higher levels of error correction means that less data can be encoded into modules. A version M4 Micro QR Code, for instance, can store 35 numeric characters at Level L, but only 21 at Level Q.
Common Use Cases
The small size of Micro QR Codes makes them ideal for small electronic components. They also fit easily onto business cards, documents, and product tags. Although Micro QR Codes are functionally similar to regular QR Codes, not all scanning devices and barcode SDKs are capable of reading them. Integrating Micro QR Code support into an application can greatly expand flexibility when it comes to tracking and managing barcoded assets.
Technical Specifications
For detailed technical information, refer to the help for your platform: